nLab vector meson
Context
Fields and quanta
fields and particles in particle physics
and in the standard model of particle physics:
matter field fermions (spinors, Dirac fields)
| flavors of fundamental fermions in the standard model of particle physics: | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| generation of fermions | 1st generation | 2nd generation | 3d generation |
| quarks () | |||
| up-type | up quark () | charm quark () | top quark () |
| down-type | down quark () | strange quark () | bottom quark () |
| leptons | |||
| charged | electron | muon | tauon |
| neutral | electron neutrino | muon neutrino | tau neutrino |
| bound states: | |||
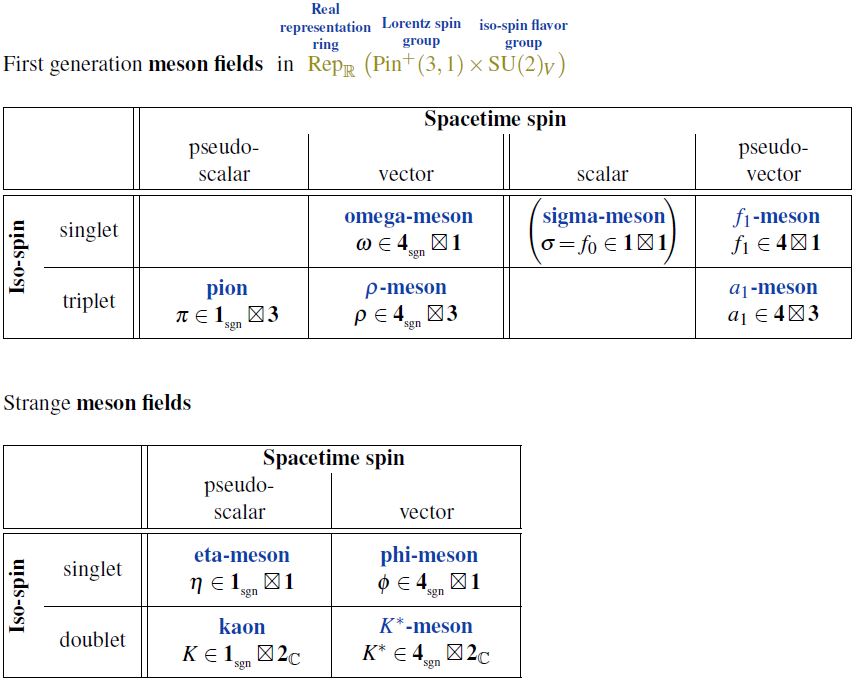
| mesons | light mesons: pion () ρ-meson () ω-meson () f1-meson a1-meson | strange-mesons: ϕ-meson (), kaon, K*-meson (, ) eta-meson () charmed heavy mesons: D-meson (, , ) J/ψ-meson () | bottom heavy mesons: B-meson () ϒ-meson () |
| baryons | nucleons: proton neutron |
(also: antiparticles)
hadrons (bound states of the above quarks)
minimally extended supersymmetric standard model
bosinos:
dark matter candidates
Exotica
Contents
Idea
A vector meson is a meson which (in Wigner classification) is in the vector representation or pseudo-vector representation of the Lorentz group.
This is in contrast to scalar mesons.
Examples
Examples of vector mesons:
Examples of pseudo-vector mesons:
Properties
Related concepts
References
(See also the references at meson.)
-
F. Nichitiu, An Introduction to the vector meson, Swansea Hadron Spect. 1995:0219-240 (spire:405666)
-
Eef van Beveren, George Rupp, Scalar and axial-vector mesons, Eur. Phys. J. A31:468-473, 2007 (arXiv:hep-ph/0610199)
See also:
- Wikipedia, Vector meson
Last revised on May 26, 2020 at 08:43:15. See the history of this page for a list of all contributions to it.